房地产网络抓取:如何像专业人士一样从 Realtor.com 提取数据
Raluca Penciuc on Apr 07 2023

Gathering accurate and up-to-date data is crucial for businesses and individuals in many industries, and real estate is no exception. Realtor.com is a popular website for finding apartments and homes for sale or rent, as it contains a wealth of information that can be valuable for real estate professionals, investors, and homebuyers.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to scrape realtor.com so you’ll have available the data you need to kickstart your project. I will walk through the process of setting up a project, navigating to realtor.com, and extracting the desired data.
I will also discuss ways to improve the reliability and efficiency of the scraper, and why using a professional scraper service may be a better option for some use cases.
By the end of this tutorial, you should have a good understanding of how to scrape realtor.com, no matter your profession: a real estate professional looking for a competitive edge, an investor seeking new opportunities, or a homebuyer searching for the perfect property.
Environment setup
Before you can start scraping, you need to install Node.js on your computer. You can download the latest version from the official website and follow the instructions according to your operating system.
Then, create a new directory for your project and navigate to it in your terminal or command prompt. Run the following command to initialize a new Node.js project:
npm init -y
这将在项目目录中创建package.json文件,其中将存储有关项目及其依赖项的信息。
To install TypeScript, run the following command:
npm install typescript -save-dev
TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript that adds optional static typing and other features. It is useful for larger projects and can make it easier to catch mistakes early on. TypeScript uses a configuration file called tsconfig.json to store compiler options and other settings. To create this file in your project, run the following command:
npx tsc -init
Make sure that the value for “outDir” is set to “dist”. This way we will separate the TypeScript files from the compiled ones.
Now, create an “src” directory in your project, and a new “index.ts” file. Here is where we will keep the scraping code. To execute TypeScript code you have to compile it first, so to make sure that we don’t forget this extra step, we can use a custom-defined command.
Head over to the “package. json” file, and edit the “scripts” section like this:
"scripts": {
"test": "npx tsc && node dist/index.js"
}这样,在执行脚本时,只需在终端中输入 "npm run test"即可。
And last but not least, run the following command to add Puppeteer to your project dependencies:
npm install puppeteer
Puppeteer is a Node.js library that provides a high-level API for controlling a headless Chrome browser, which can be used for web scraping and automation tasks. It is highly recommended when you want to ensure the completeness of your data, as many websites today contain dynamic-generated content.
Data selection
Now that you have your environment set up, we can start looking at extracting the data. For this article, I chose to scrape the list of studio apartments available for rent in Plano, TX: https://www.realtor.com/apartments/Plano_TX/beds-studio.
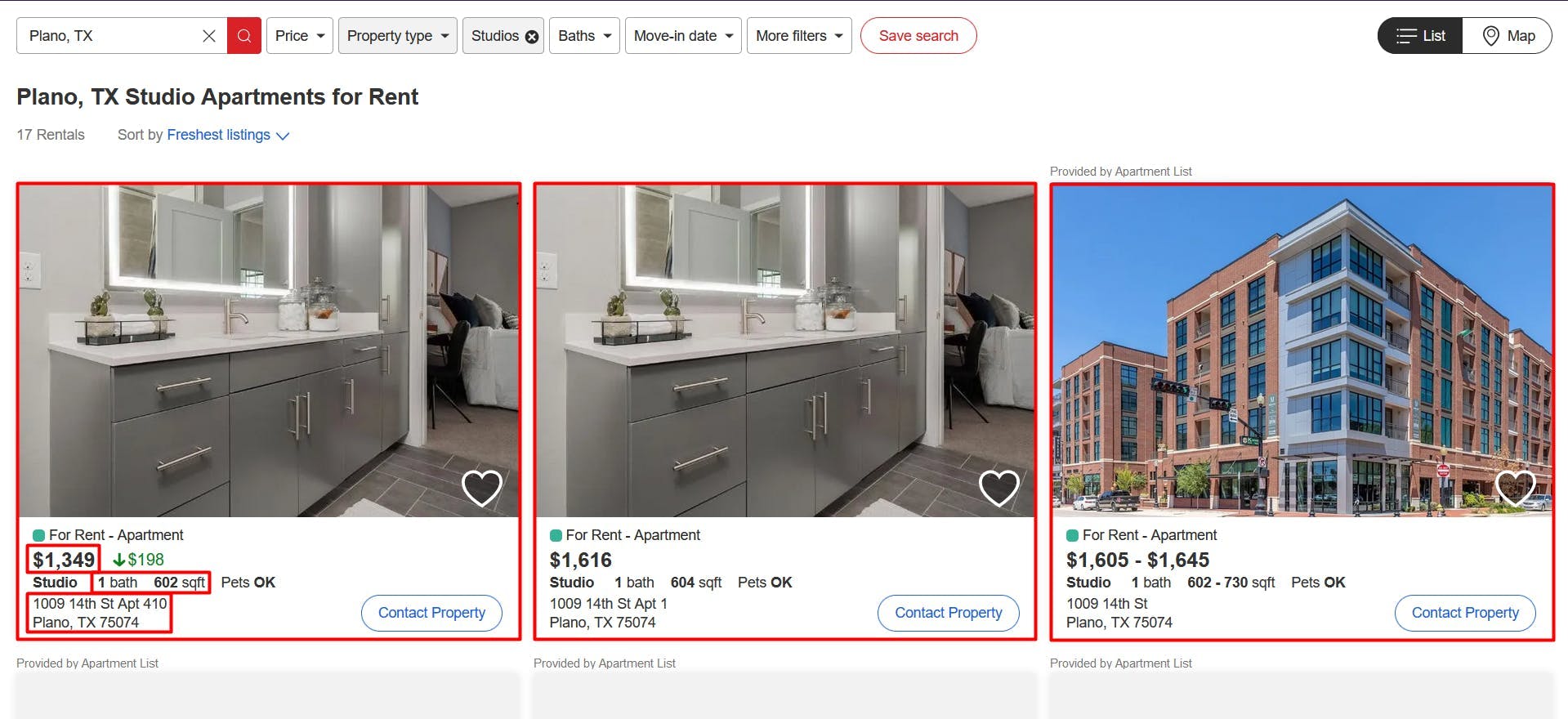
We’re going to extract the following data from each listing on the page:
- the URL;
- the prices;
- the number of baths;
- the surfaces (measured in square feet);
- the physical addresses
您可以在下面的截图中看到所有这些信息:
数据提取
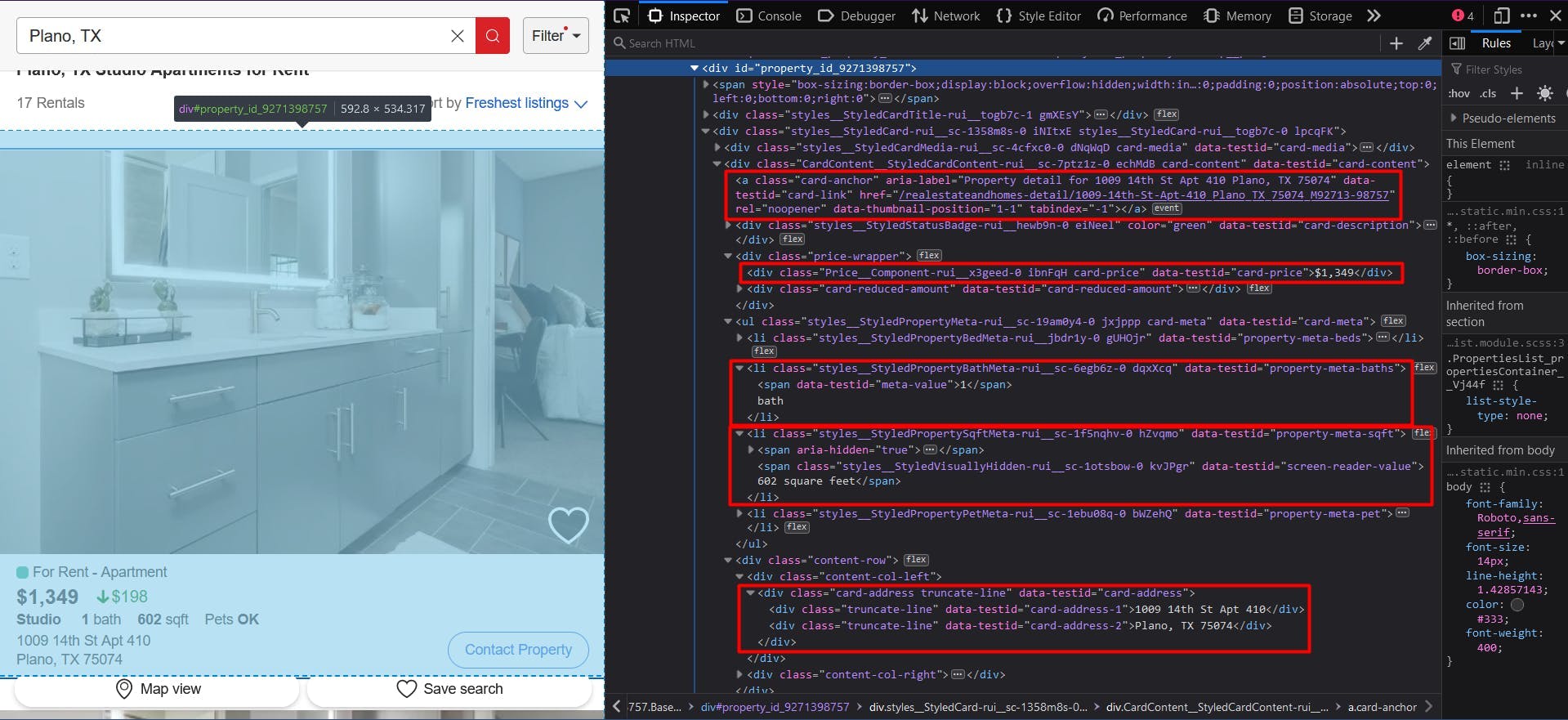
To extract all this data, we’ll need to locate it first. Right-click on the highlighted sections, then choose “Inspect” to open the Developer Tools and see the HTML document. By moving the mouse cursor over it, you can easily see what part corresponds to each section:
For this tutorial, I’ll be using CSS selectors, as they are the most straightforward option. If you are new to this method, feel free to check out this self-explanatory guide first.
To start writing our script, let’s verify that the Puppeteer installation went alright:
import puppeteer from 'puppeteer';
async function scrapeRealtorData(realtor_url: string): Promise<void> {
// Launch Puppeteer
const browser = await puppeteer.launch({
headless: false,
args: ['--start-maximized'],
defaultViewport: null
})
const page = await browser.newPage()
// Navigate to the channel URL
await page.goto(realtor_url)
// Close the browser
await browser.close()
}
scrapeRealtorData("https://www.realtor.com/apartments/Plano_TX/beds-studio")
Here we open a browser window, create a new page, navigate to our target URL and then close the browser. For the sake of simplicity and visual debugging, I open the browser maximized in non-headless mode.
Because each listing has the same structure and the same data, in our algorithm we’ll extract every piece of information for the whole properties list. At the end of the script, we’ll iterate through all the results and centralize them in a single list.
You may have noticed that the listing URL was not visible in the first screenshot, but it was mentioned and highlighted in the second one. That’s because you are redirected to the property’s URL when you click on it.
// Extract listings location
const listings_location = await page.evaluate(() => {
const locations = document.querySelectorAll('a[data-testid="card-link"]')
const locations_array = Array.from(locations)
return locations ? locations_array.map(a => a.getAttribute('href')) : []
})
console.log(listings_location)
We locate the URL by choosing the anchor elements that have the “data-testid” attribute with the “card-link” value. Then we convert the result to a JavaScript array and map each element to the value of the “href” attribute.
However, the resulting list will contain each URL twice. That’s because each listing has the same anchor element for 2 sections: the property pictures and its renting details. We can easily fix this by using the Set data structure:
const unique_listings_location = [...new Set(listings_location)]
console.log(unique_listings_location)
For the property price, we will extract the “div” elements that have the “data-testid” attribute with the “card-price” value. It needs to be converted to an array as well and then mapped to its text content.
// Extract listings price
const listings_price = await page.evaluate(() => {
const prices = document.querySelectorAll('div[data-testid="card-price"]')
const prices_array = Array.from(prices)
return prices ? prices_array.map(p => p.textContent) : []
})
console.log(listings_price)
To get the number of baths and the property surface, we will use the operator for direct child elements. This means that the parent element is uniquely identified, while the child element has a more generic id or class name. Apart from that, the logic is the same as before:
// Extract listings baths
const listings_baths = await page.evaluate(() => {
const baths = document.querySelectorAll('li[data-testid="property-meta-baths"] > span[data-testid="meta-value"]')
const baths_array = Array.from(baths)
return baths ? baths_array.map(b => b.textContent) : []
})
console.log(listings_baths)
// Extract listings sqft
const listings_sqft = await page.evaluate(() => {
const sqfts = document.querySelectorAll('li[data-testid="property-meta-sqft"] > span[data-testid="screen-reader-value"]')
const sqfts_array = Array.from(sqfts)
return sqfts ? sqfts_array.map(s => s.textContent) : []
})
console.log(listings_sqft)
And finally, for the addresses of the listings, we pick the “div” elements that have the “data-testid” attribute” set to the “card-address” value.
// Extract listings address
const listings_address = await page.evaluate(() => {
const addresses = document.querySelectorAll('div[data-testid="card-address"]')
const addresses_array = Array.from(addresses)
return addresses ? addresses_array.map(a => a.textContent) : []
})
console.log(listings_address)
Now you should have 5 lists, one for each piece of data we scraped. As I mentioned before, we should centralize them into a single one. This way, the information we gathered will be much easier to further process.
// Group the lists
const listings = []
for (let i = 0; i < unique_listings_location.length; i++) {
listings.push({
url: unique_listings_location[i],
price: listings_price[i],
baths: listings_baths[i],
sqft: listings_sqft[i],
address: listings_address[i]
})
}
console.log(listings)
The final result should look something like this:
[
{
url: '/realestateandhomes-detail/1009-14th-St-Apt-410_Plano_TX_75074_M92713-98757',
price: '$1,349',
baths: '1',
sqft: '602 square feet',
address: '1009 14th St Apt 410Plano, TX 75074'
},
{
url: '/realestateandhomes-detail/1009-14th-St-Apt-1_Plano_TX_75074_M95483-11211',
price: '$1,616',
baths: '1',
sqft: '604 square feet',
address: '1009 14th St Apt 1Plano, TX 75074'
},
{
url: '/realestateandhomes-detail/1009-14th-St_Plano_TX_75074_M87662-45547',
price: '$1,605 - $2,565',
baths: '1 - 2',
sqft: '602 - 1,297 square feet',
address: '1009 14th StPlano, TX 75074'
},
{
url: '/realestateandhomes-detail/5765-Bozeman-Dr_Plano_TX_75024_M70427-45476',
price: '$1,262 - $2,345',
baths: '1 - 2',
sqft: '352 - 1,588 square feet',
address: '5765 Bozeman DrPlano, TX 75024'
},
{
url: '/realestateandhomes-detail/1410-K-Ave-Ste-1105A_Plano_TX_75074_M97140-46163',
price: '$1,250 - $1,995',
baths: '1 - 2',
sqft: '497 - 1,324 square feet',
address: '1410 K Ave Ste 1105APlano, TX 75074'
}
]
Avoid bot detection
While scraping Realtor may seem easy at first, the process can become more complex and challenging as you scale up your project. The real estate website implements various techniques to detect and prevent automated traffic, so your scaled-up scraper starts getting blocked.
Realtor uses the “Press & Hold” model of CAPTCHA, offered by PerimeterX, which is known to be almost impossible to solve from your code. Besides this, the website also collects multiple browser data to generate and associate you with a unique fingerprint.
在收集到的浏览器数据中,我们发现
- Navigator 对象的属性(deviceMemory、hardwareConcurrency、languages、platform、userAgent、webdriver 等)。
- 时间和性能检查
- WebGL
- WebRTC IP sniffing
- 以及更多
One way to overcome these challenges and continue scraping at large scale is to use a scraping API. These kinds of services provide a simple and reliable way to access data from websites like Realtor.com, without the need to build and maintain your own scraper.
WebScrapingAPI 就是这样一款产品。它的代理旋转机制完全避免了验证码,其扩展知识库可以随机化浏览器数据,使其看起来像真实用户。
设置简单快捷。你只需注册一个账户,就会收到 API 密钥。您可以在仪表板上访问该密钥,它用于验证您发送的请求。
由于您已经设置了 Node.js 环境,我们可以使用相应的 SDK。运行以下命令将其添加到项目依赖项中:
npm install webscrapingapi
现在只需根据 API 调整之前的 CSS 选择器即可。提取规则的强大功能使我们可以在不做重大修改的情况下解析数据。
import webScrapingApiClient from 'webscrapingapi';
const client = new webScrapingApiClient("YOUR_API_KEY");
async function exampleUsage() {
const api_params = {
'render_js': 1,
'proxy_type': 'datacenter',
'timeout': 60000,
'extract_rules': JSON.stringify({
locations: {
selector: 'a[data-testid="card-link"]',
output: '@href',
all: '1'
},
prices: {
selector: 'div[data-testid="card-price"]',
output: 'text',
all: '1'
},
baths: {
selector: 'li[data-testid="property-meta-baths"] > span[data-testid="meta-value"]',
output: 'text',
all: '1'
},
sqfts: {
selector: 'li[data-testid="property-meta-sqft"] > span[data-testid="screen-reader-value"]',
output: 'text',
all: '1'
},
addresses: {
selector: 'div[data-testid="card-address"]',
output: 'text',
all: '1'
}
})
}
const URL = "https://www.realtor.com/apartments/Plano_TX/beds-studio"
const response = await client.get(URL, api_params)
if (response.success) {
const unique_listings_location = [...new Set(response.response.data.locations)]
// Group the lists
const listings = []
for (let i = 0; i < unique_listings_location.length; i++) {
listings.push({
url: unique_listings_location[i],
price: response.response.data.prices[i],
baths: response.response.data.baths[i],
sqft: response.response.data.sqfts[i],
address: response.response.data.addresses[i]
})
}
console.log(listings)
} else {
console.log(response.error.response.data)
}
}
exampleUsage();
结论
In this tutorial, we have provided a step-by-step guide on how to scrape realtor.com using Node.js and Puppeteer. We have also discussed ways to improve the reliability and efficiency of the scraper, and why using a professional scraper service may be a better option for some use cases.
Realtor.com is a popular and valuable source of real estate data, and with the skills and knowledge you have gained in this tutorial, you should now be able to use web scraping to extract this data and put it to use in your own projects.
Whether you are a real estate professional looking for a competitive edge, an investor seeking new opportunities, or a homebuyer searching for the perfect property, web scraping can provide you with valuable insights and data from realtor.com. We hope this tutorial has been helpful and that you are now ready to elevate your real estate game with the help of web scraping from realtor.com.

相关文章

通过我们的深入指南,探索刮擦亚马逊产品数据的复杂性。从最佳实践和亚马逊 Scraper API 等工具到法律注意事项,了解如何应对挑战、绕过验证码并高效提取有价值的见解。


详细比较 Scrapy 和 Beautiful Soup 这两个领先的网络搜刮工具。了解它们的功能、优缺点,并探索如何将它们结合使用以满足各种项目需求。


