解析:如何用 Python 从 HTML 中提取文本
米哈伊-马克西姆(Mihai Maxim),2023 年 1 月 31 日

导言
Web scraping 是通过使用脚本或程序从网站收集数据的自动化过程。它用于提取文本、图像等信息以及其他类型的数据,这些数据可用于研究、数据分析或市场分析等不同目的。
如今,使用 Python 进行网络刮擦有很多解决方案。Selenium 和 Scrapy 是其中使用最广泛、最流行的库。虽然这些工具非常适合复杂的刮擦任务,但对于普通用户来说,它们可能有点难以承受。
进入 Parsel--小型网络搜索库。这个轻量级的库简单易学,非常适合小型项目,也非常适合网络搜索新手。它能使用 CSS 和 XPath 选择器解析 HTML 并提取数据,是任何数据爱好者寻找快速、简便的网络信息收集方法的绝佳工具。
系好安全带,准备好学习如何使用这个库,和我一起踏上自动数据收集的冒险之旅。让我们开始搜刮吧!
开始使用 Parsel
您可以使用以下命令安装 Parsel 库:
pip install parsel
现在,让我们直接进入一个示例项目,从这个简单的网站https://www.scrapethissite.com/pages/simple/ 中抓取所有国家的数据。
要从网站上获取 HTML,您需要发出 HTTP GET 请求。
我们将使用 "requests "Python 库进行 HTTP 请求,因此请确保安装了该库:
pip install requests
现在你可以获取 HTML,并将其写入文件:
import parsel
import requests
response = requests.get("https://www.scrapethissite.com/pages/simple/")
with open("out.html", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(response.text)
并检查结构:
我们的数据存储在类似的结构中:
<div class="col-md-4 country">
<h3 class="country-name">
<i class="flag-icon flag-icon-af"></i>
Afghanistan
</h3>
<div class="country-info">
<strong>Capital:</strong> <span class="country-capital">Kabul</span><br>
<strong>Population:</strong> <span class="country-population">29121286</span><br>
<strong>Area (km<sup>2</sup>):</strong> <span class="country-area">647500.0</span><br>
</div>
</div><!--.col-->
为了编写选择器,您需要将原始 HTML 传递给 Parsel:
import parsel
import requests
response = requests.get("https://www.scrapethissite.com/pages/simple/")
raw_html = response.text
parsel_dom = parsel.Selector(text = raw_html)
现在,我们可以编写一些选择器了。
使用 CSS 选择器提取文本
您可以打印第一个国家的首都:
parsel_dom = parsel.Selector(text=raw_html)
first_capital = parsel_dom.css(".country-capital::text").get()
print(first_capital)
// 输出
Andorra la Vella
parsel_dom.css(".country-capital::text").get() 将选择具有 country-capital 类的第一个元素的内部文本。您可以打印所有国家的名称:
countries_names = filter(lambda line: line.strip() != "", parsel_dom.css(".country-name::text").getall())
for country_name in countries_names:
print(country_name.strip())
// Output
Andorra
United Arab Emirates
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Anguilla
..parsel_dom.css(".country-name::text").getall() 将选择所有具有 "country-name "类的元素的内部文本。 Notice that we had to clean-up the output a bit. We did that because all the elements that have the “.country-name” class also have an <i> tag nested inside of them. Also, the country name is surrounded by many trailing spaces.
<h3 class="country-name">
<i class="flag-icon flag-icon-ae"></i> //this is picked up as an empty string
United Arab Emirates // this is picked up as “ United Arab Emirates “
</h3>
现在,让我们编写一个脚本,用 CSS 选择器提取所有数据:
import parsel
import requests
response = requests.get("https://www.scrapethissite.com/pages/simple/")
raw_html = response.text
parsel_dom = parsel.Selector(text=raw_html)
countries = parsel_dom.css(".country")
countries_data = []
for country in countries:
country_name = country.css(".country-name::text").getall()[1].strip()
country_capital = country.css(".country-capital::text").get()
country_population = country.css(".country-population::text").get()
country_area = country.css(".country-area::text").get()
countries_data.append({
"name": country_name,
"capital": country_capital,
"population": country_population,
"area": country_area
})
for country_data in countries_data:
print(country_data)
// Outputs
{'name': 'Andorra', 'capital': 'Andorra la Vella', 'population': '84000', 'area': '468.0'}
{'name': 'United Arab Emirates', 'capital': 'Abu Dhabi', 'population': '4975593', 'area': '82880.0'}
{'name': 'Afghanistan', 'capital': 'Kabul', 'population': '29121286', 'area': '647500.0'}
...
使用 XPath 选择器提取文本
XPath 是一种查询语言,用于从 XML 文档中选择节点。它是 XML 路径语言(XML Path Language)的缩写,使用与 URL 类似的路径符号来浏览 XML 文档中的元素和属性。XPath 表达式可用于选择单个元素、一组元素或元素的特定属性。XPath 主要用于 XSLT,但也可用于浏览任何类似 XML 语言文档(如 HTML 或 SVG)的文档对象模型(DOM)。
XPath 一开始看起来很吓人,但实际上只要了解了基本概念和语法,上手还是很容易的。我们的 XPath 选择器指南(https://www.webscrapingapi.com/the-ultimate-xpath-cheat-sheet)就是一个很有用的资源。
现在,让我们试试一些选择器:
下面是打印第一个大写字母的方法:
parsel_dom = parsel.Selector(text=raw_html)
first_capital = parsel_dom.xpath('//*[@class="country-capital"]/text()').get()
print(first_capital)
// 输出
Andorra la Vella
还有所有的国名:
countries_names = filter(lambda line: line.strip() != "",
parsel_dom.xpath('//*[@class="country-name"]//text()').getall())
for country_name in countries_names:
print(country_name.strip())
// Output
Andorra la Vella
Abu Dhabi
Kabul
St. John's
The Valley
Tirana
...
让我们用 XPath 选择器重新实现脚本:
import parsel
import requests
response = requests.get("https://www.scrapethissite.com/pages/simple/")
raw_html = response.text
parsel_dom = parsel.Selector(text=raw_html)
countries = parsel_dom.xpath('//div[contains(@class,"country")][not(contains(@class,"country-"))]')
countries_data = []
for country in countries:
country_name = country.xpath(".//h3/text()").getall()[1].strip()
country_capital = country.xpath(".//span/text()").getall()[0]
country_population = country.xpath(".//span/text()").getall()[1]
country_area = country.xpath(".//span/text()").getall()[2]
countries_data.append({
"name": country_name,
"capital": country_capital,
"population": country_population,
"area": country_area
})
for country_data in countries_data:
print(country_data)
// Output
{'name': 'Andorra', 'capital': 'Andorra la Vella', 'population': '84000', 'area': '468.0'}
{'name': 'United Arab Emirates', 'capital': 'Abu Dhabi', 'population': '4975593', 'area': '82880.0'}
{'name': 'Afghanistan', 'capital': 'Kabul', 'population': '29121286', 'area': '647500.0'}
...
删除元素
删除元素非常简单。只需将下拉功能应用于选择器即可:
selector.css(".my_class").drop()让我们编写一个脚本,删除每个国家的 "人口 "文件,来展示这一功能:
import parsel
import requests
response = requests.get("https://www.scrapethissite.com/pages/simple/")
raw_html = response.text
parsel_dom = parsel.Selector(text=raw_html)
countries = parsel_dom.css(".country")
for country in countries:
country.css(".country-population").drop()
country.xpath(".//strong")[1].drop()
country.xpath(".//br")[1].drop()
countries_without_population_html = parsel_dom.get()
with open("out.html", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(countries_without_population_html)
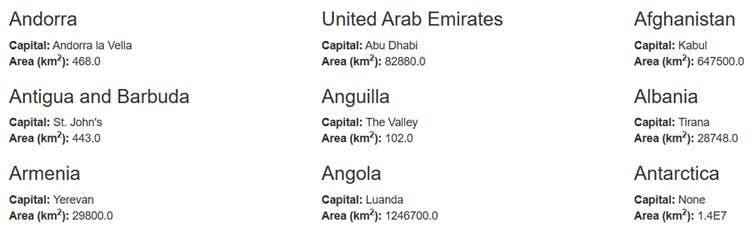
导出数据
完成数据采集后,重要的是考虑如何保存数据。存储此类数据的两种常见格式是 .json 和 .csv。不过,您应该根据自己的项目需求选择最合适的格式。
将数据导出为 .json
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation,JavaScript 对象符号)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,它便于人类读写,也便于机器解析和生成。它通常用于在网络应用程序和服务器之间或网络应用程序的不同部分之间交换数据。JSON 类似于 Python 字典,它用于以键值对的形式存储数据,可用于存储和访问相同类型的数据,并具有相同的结构。
使用 json 库可以将 Python 字典数组导出为 .json 格式:
import json
countries_dictionaries = [
{'name': 'Andorra', 'capital': 'Andorra la Vella', 'population': '84000', 'area': '468.0'},
{'name': 'United Arab Emirates', 'capital': 'Abu Dhabi', 'population': '4975593', 'area': '82880.0'}
]
json_data = json.dumps(countries_dictionaries, indent=4)
with open("data.json", "w") as outfile:
outfile.write(json_data)
// data.json
[
{
"name": "Andorra",
"capital": "Andorra la Vella",
"population": "84000",
"area": "468.0"
},
{
"name": "United Arab Emirates",
"capital": "Abu Dhabi",
"population": "4975593",
"area": "82880.0"
}
]
将数据导出为 .csv 格式
CSV 是一种在文本文件中存储数据的简单方法,每行代表一行,每个值用逗号分隔。它通常用于电子表格或数据库程序。Python 通过其 csv 模块为处理 CSV 文件提供了强大的内置支持。CSV 模块最强大的功能之一是 DictWriter 类,它允许您以简单的方式将 Python 字典写入 CSV 文件。字典的键将用作 CSV 文件中的列标题,而值将作为相应数据写入行中。
下面介绍如何使用 csv 库将 Python 字典数组导出为 .csv。
countries_dictionaries = [
{"name": "John Smith", "age": 35, "city": "New York"},
{"name": "Jane Doe", "age": 28, "city": "San Francisco"}
]
with open("data.csv", "w") as outfile:
writer = csv.DictWriter(outfile, fieldnames=countries_dictionaries[0].keys())
writer.writeheader()
for row in countries_dictionaries:
writer.writerow(row)
// data.csv
name,age,city
John Smith,35,New York
Jane Doe,28,San Francisco
总结
在本文中,我们探索了 Python 中 Parsel 库的使用。我们看到了使用 Parsel 提供的 CSS 和 XPath 选择器从网页中提取数据是多么容易。总之,Parsel 为网页刮擦提供了一个高效、通用的解决方案。如果你对自动化数据收集感兴趣,一定要试试。
您想了解更多有关网络抓取的信息吗?请查看我们的产品 WebScrapingAPI,了解如何将您的数据提取技能提升到新的水平。我们功能强大的 API 专为帮助您克服网络搜刮中最常见的挑战而设计,例如避免 IP 禁止或渲染 Javascript。最棒的是什么?您可以免费试用!

相关文章

通过我们的深入指南,探索刮擦亚马逊产品数据的复杂性。从最佳实践和亚马逊 Scraper API 等工具到法律注意事项,了解如何应对挑战、绕过验证码并高效提取有价值的见解。




